OMEGA 3 AND VIRTUES
What are omega-3s?
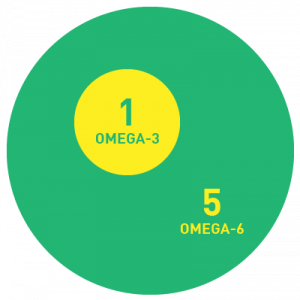
Omega-3s are a family of so-called essential fatty acids that participate in the structure of cell membranes (particularly in the brain) and in the balance of physiological reactions in the body. They give cell membranes great fluidity, facilitating cellular communication. In addition, they partly control the body’s inflammation reactions and prevent them from becoming excessive.
The three main omega-3s are :
- Alpha-linolenic acid (18:3, ALA): it is mainly found in vegetable oils such as linseed and rapeseed oil. It is described as indispensable, because our body needs it and cannot synthesise it itself.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5, EPA): plays an important role in mediating certain biological agents, by attenuating the inflammatory response, increasing blood fluidity and reducing triglyceride levels.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (22:6, DHA): A component of nerve cells, it plays an important role in membrane structure and the development and function of the brain and retina.
Khan, Mala & Rahman, Md & Zaman, Shanza & Jahangir, Arif & Razu, Mamudul. (2015). Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Algae.